Indications
- Abdominal wall lacerations or injuries
- Abdominal wall abscess incision and drainage
Contraindications
- Infection overlying injection site
- Allergy to local anesthetic
Equipment
- 10cc of local anesthetic of choice diluted with 5-10cc of normal saline
- 20-22G needle (or spinal needle)
- Cleansing solution
- Ultrasound with high-frequency linear transducer
- Ultrasound transducer sterile cover
Preparation
Position
Position the patient supine
Ultrasound
Landmarks
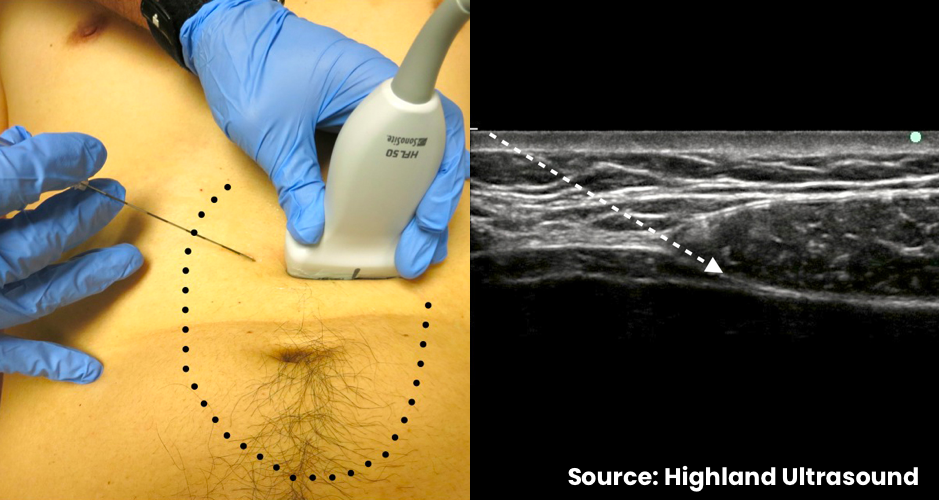
- Position the transducer in transverse orientation cephalad and lateral to the umbilicus
- Identify the linea alba and the anterior and posterior portions of the rectus sheath surrounding the rectus abdominis muscle
- Use color Doppler to identify and avoid epigastric arteries
Technique
- In-plane needle visualization
- Enter from medial-to-lateral
- Advance needle towards the posterior rectus sheath
- Inject small aliquots of local anesthetic or normal saline to confirm correct position (between rectus abdominis muscle and posterior rectus sheath)
- Deposit remainder of local anesthetic
- Repeat on contralateral side