Indications
- Fractures of distal tibia/fibula, foot fractures
- Achilles tendon rupture
- Lower extremity burns, lacerations and abscesses
Contraindications
- Infection overlying injection site
- Allergy to local anesthetic
- Request of consultant
- Concern for compartment syndrome
Equipment
- 15-20cc of local anesthetic of choice
- 20-22G needle
- Cleansing solution
- Ultrasound with high-frequency linear transducer
- Ultrasound transducer sterile cover
Ultrasound
Position
Position the patient prone
Ultrasound
Landmarks
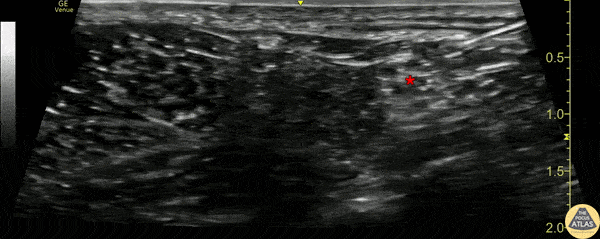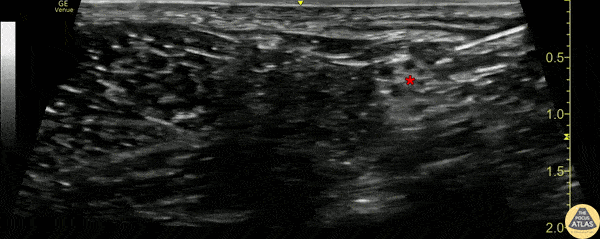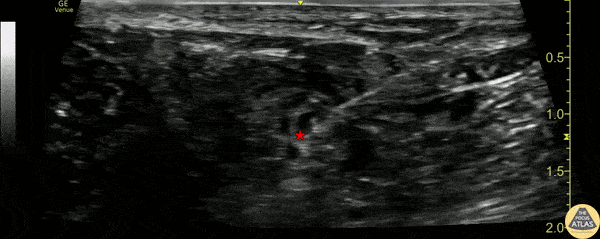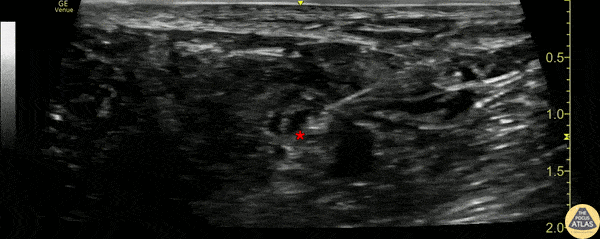
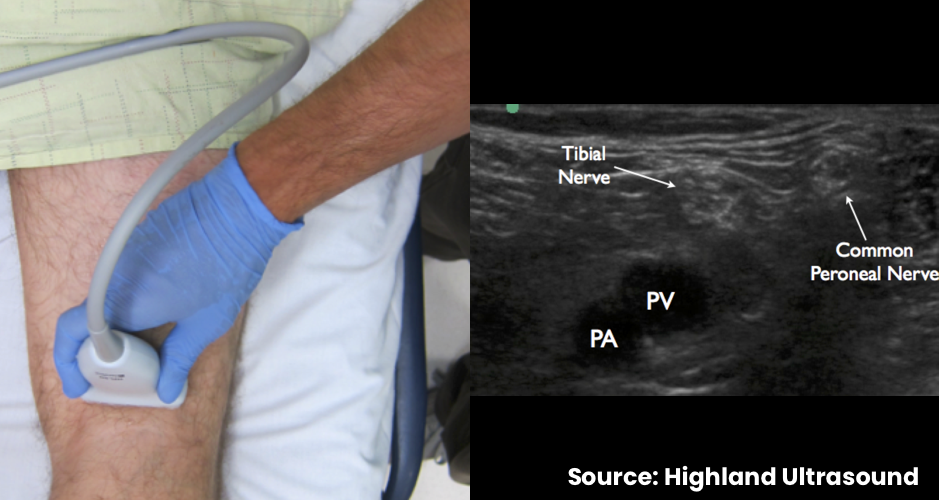
- Place the transducer in a transverse orientation in the popliteal fossa
- Identify the popliteal artery and vein
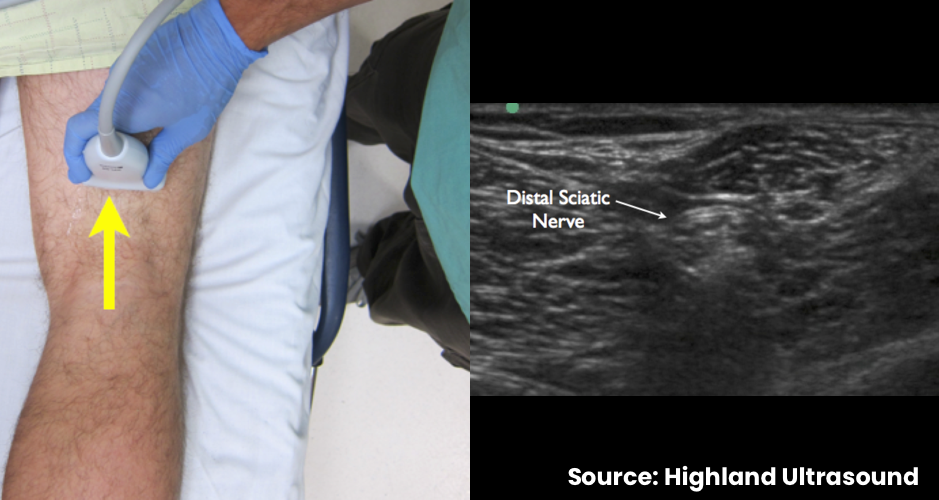
- Translate cephalad to observe the common peroneal nerve and tibial nerve joining to form the distal sciatic nerve
Technique
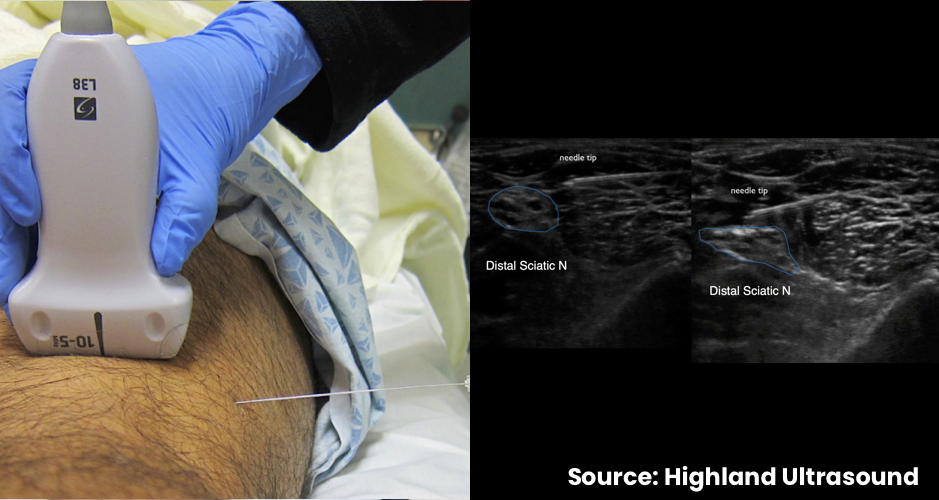
- Introduce needle lateral to medial
- In-plane needle visualization aided by flat angle-of-entry
- Gently inject local anesthetic around the nerve bundle
Examples