Indications
- Intertrochanteric hip and femoral neck fractures
- Acetabulum and pubic rami fractures
Contraindications
- Infection overlying injection site
- Allergy to local anesthetic
Target
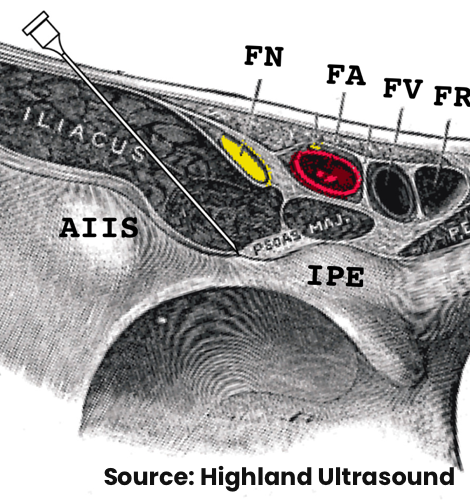
- Pericapsular nerve group (PENG)
- Lumbar plexus branches contributing to pelvis innervation and possible targets of high-volume PENG block
- Femoral nerve (including articular branch)
- Obturator nerve (including accessory obturator nerve)
Equipment
- 20cc of local anesthetic of choice
- 20G spinal needle
- Saline Flush
- Cleansing solution
- Ultrasound with low-frequency curvilinear transducer
- Ultrasound with high-frequency linear transducer (for small body habitus)
- Ultrasound transducer sterile cover
Preparation
Anatomy
Position
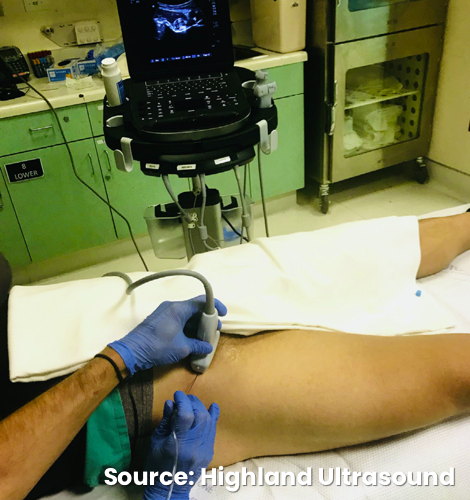
Position the patient supine
Ultrasound
Landmarks
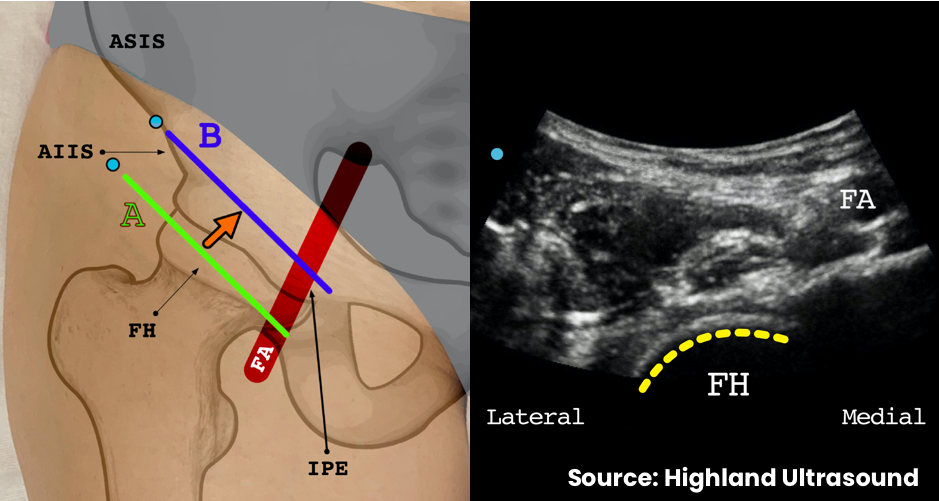
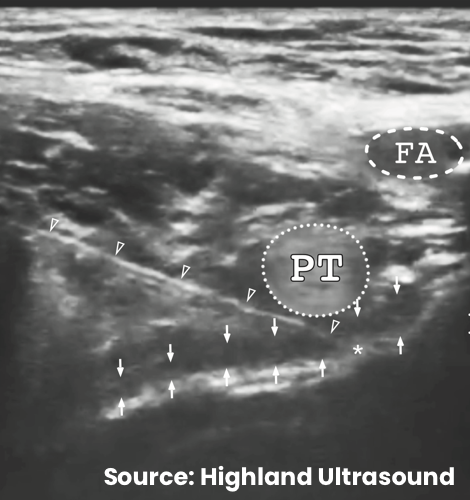
- Place the transducer in a transverse orientation on the proximal thigh parallel and adjacent to inguinal ligament (rotated approximately 45°)
- Identify the femoral artery and the femoral head
- Keep the femoral artery in view and translate transducer cephalad to bring the ilium into view
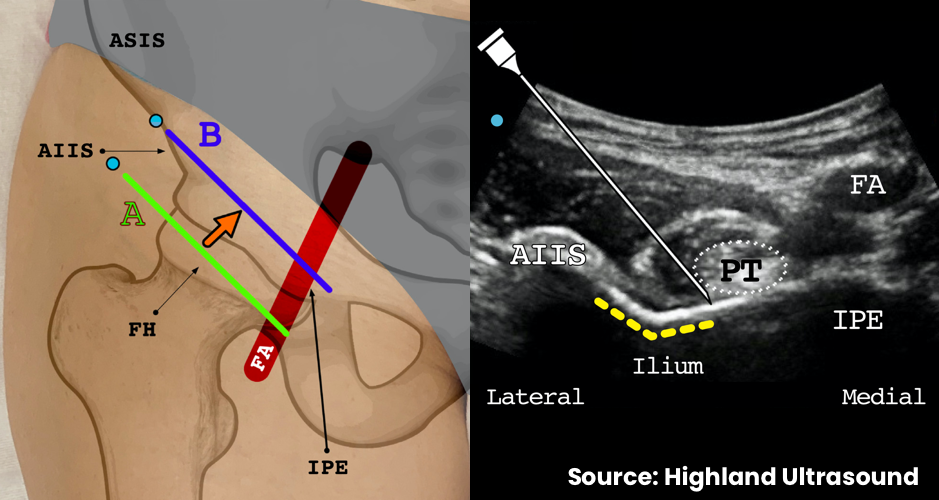
- Identify the anterior inferior iliac spine and iliopubic eminence
- The injection target is the bony surface of the ilium lateral to the psoas tendon
Technique
- Create a local anesthetic skin wheal at the insertion site
- Enter lateral-to-medial at 30-45° angle with in-plane needle visualization
- Pass through the iliopsoas to the injection target deep and just lateral to the psoas tendon
- Contact the bony surface of the ilium
- With the needle tip resting against the ilium, rotate the needle to assist with complete puncture through the fascia of the psoas
- Confirm appropriate position with injection of small aliquots of normal saline (total 10cc) which should demonstrate fluid spreading adjacent to bone, deep to the psoas fascia, and elevating the iliopsoas muscle and psoas tendon
- Slowly inject local anesthetic