Indications
- Hand laceration or injury
Contraindications
- Infection overlying injection site
- Allergy to local anesthetic
- Vascular injury/injection: blocking proximal to elbow the median nerve runs with the brachial artery, ensure a negative aspiration prior to injection
Equipment
- 5cc of local anesthetic of choice
- 25-27G needle
- Saline Flush
- Cleansing solution
- Ultrasound with high-frequency linear transducer
- Ultrasound transducer sterile cover
Prepration
Position
Position patient supine with arm abducted to expose the volar forearm.
Ultrasound
Approach #1 (Elbow)
- Place the transducer on the radial aspect of the upper arm 2-3cm proximal to the elbow crease.
- Identify the brachial artery, the median nerve is just medial to the brachial artery.
- Insert the needle in-plane from the radial aspect until the needle tip is adjacent to the nerve.
- After negative aspiration, hydrodissect 1-2 mLs of anesthetic to confirm placement, then inject anesthetic until the nerve is surrounded.
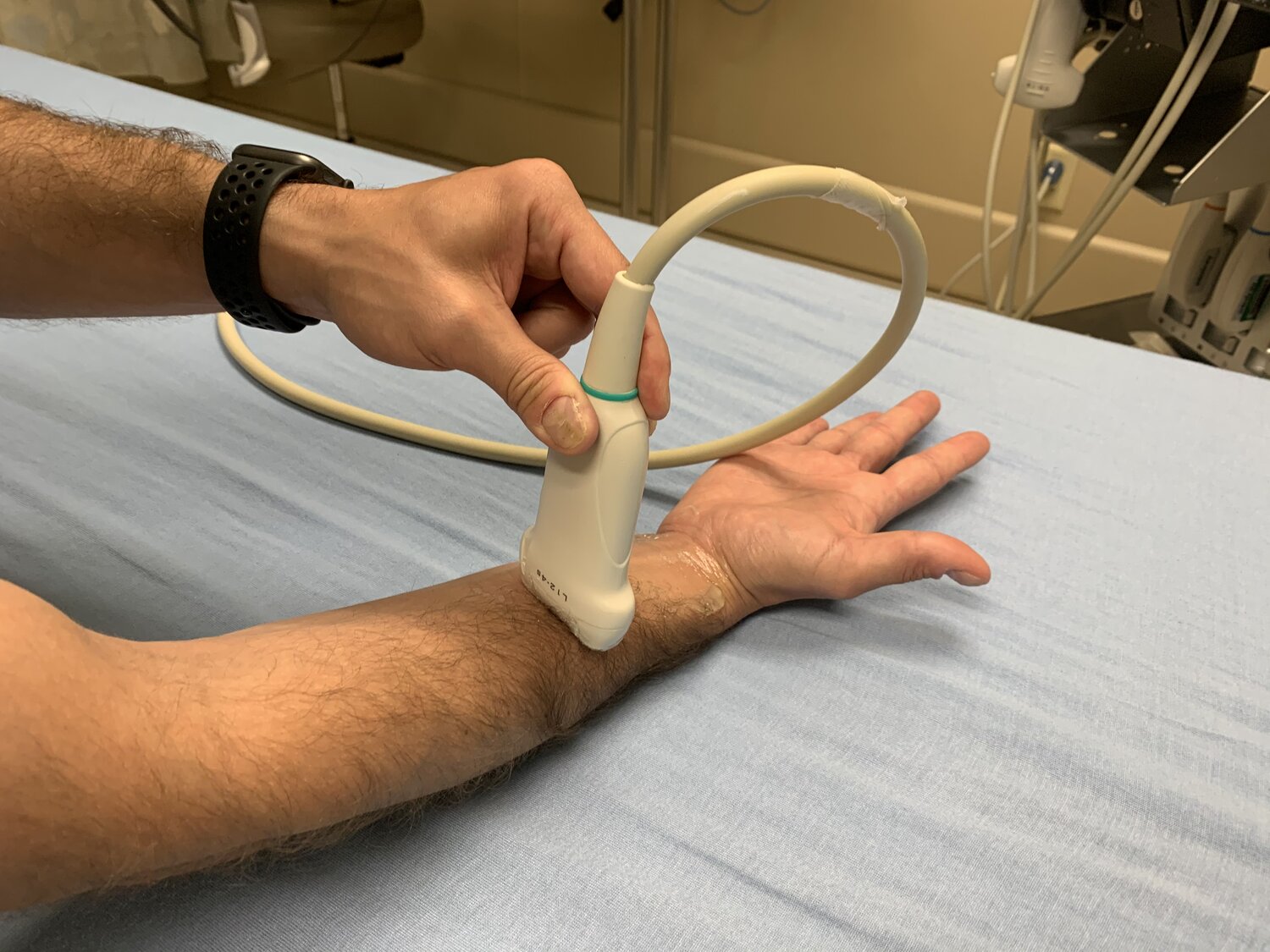
Approach #2 (Wrist)
- Place the transducer in transverse orientation over the midpoint of the forearm.
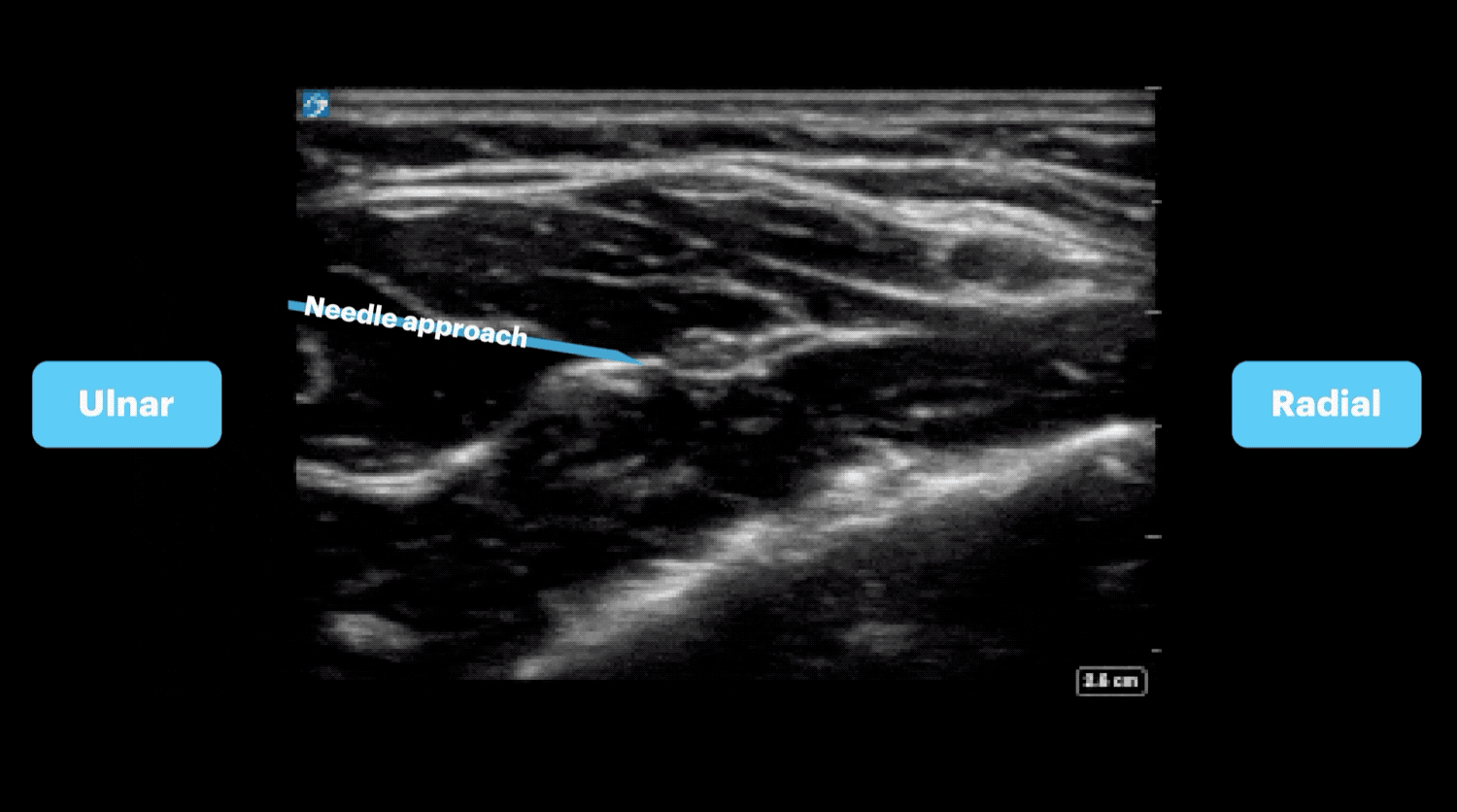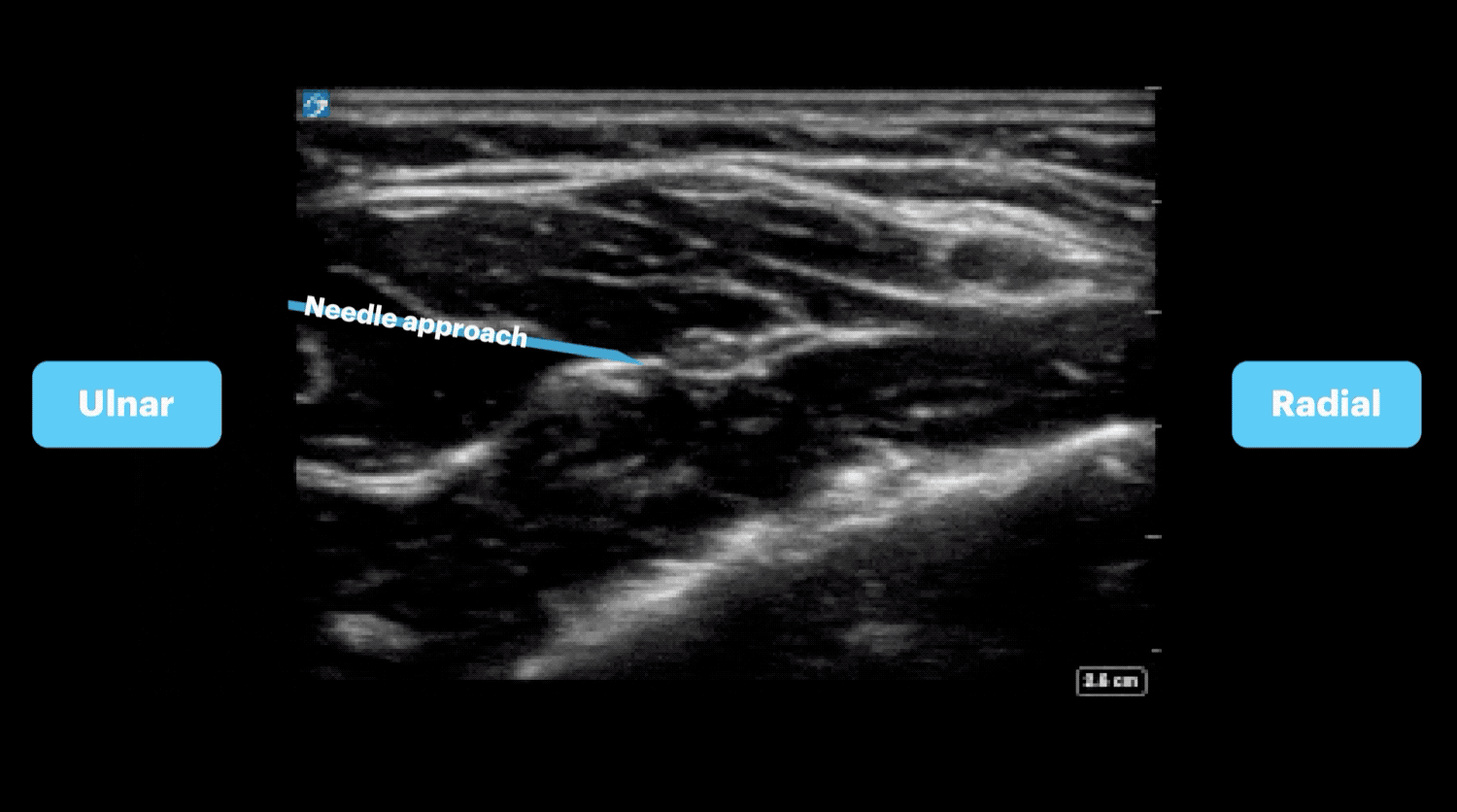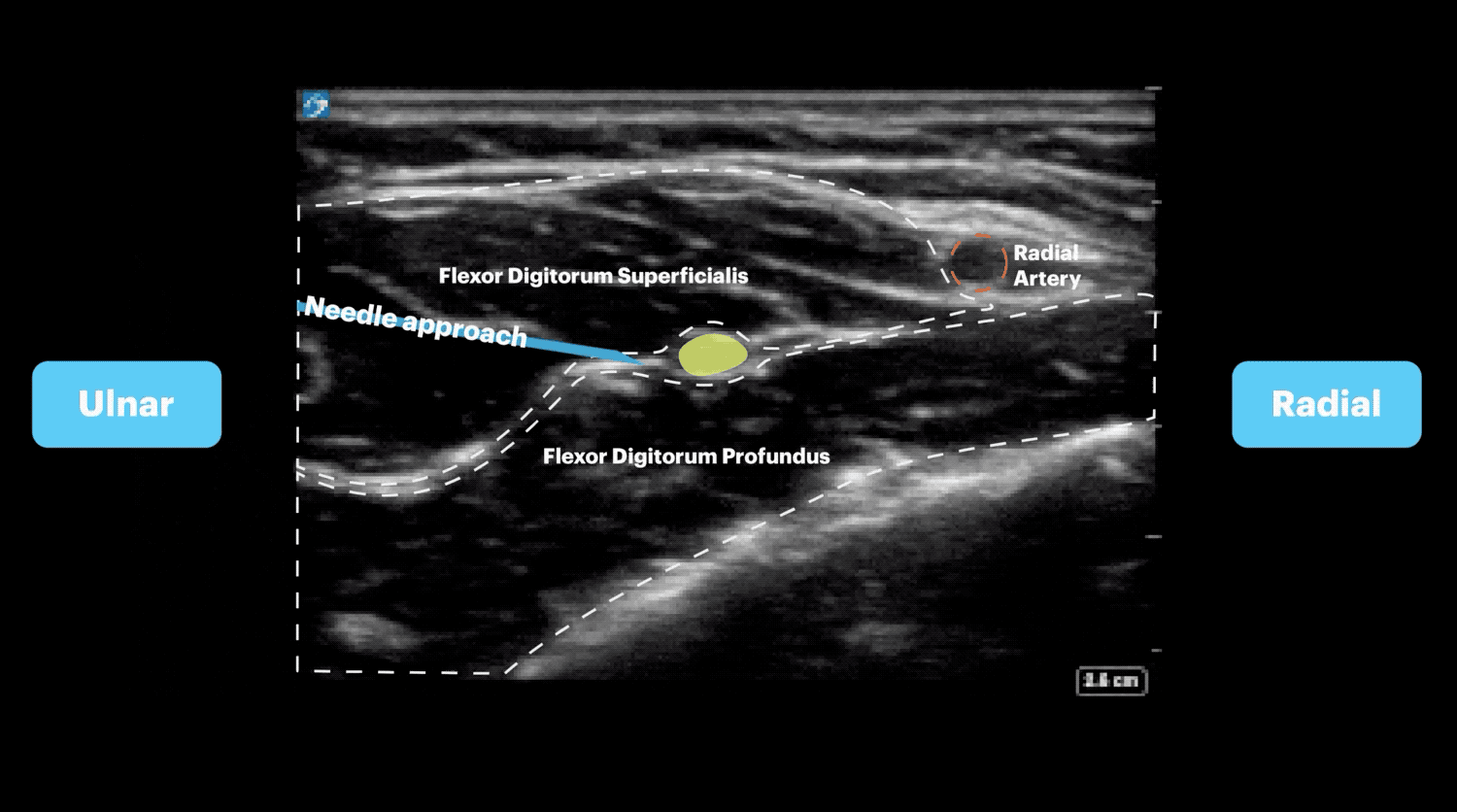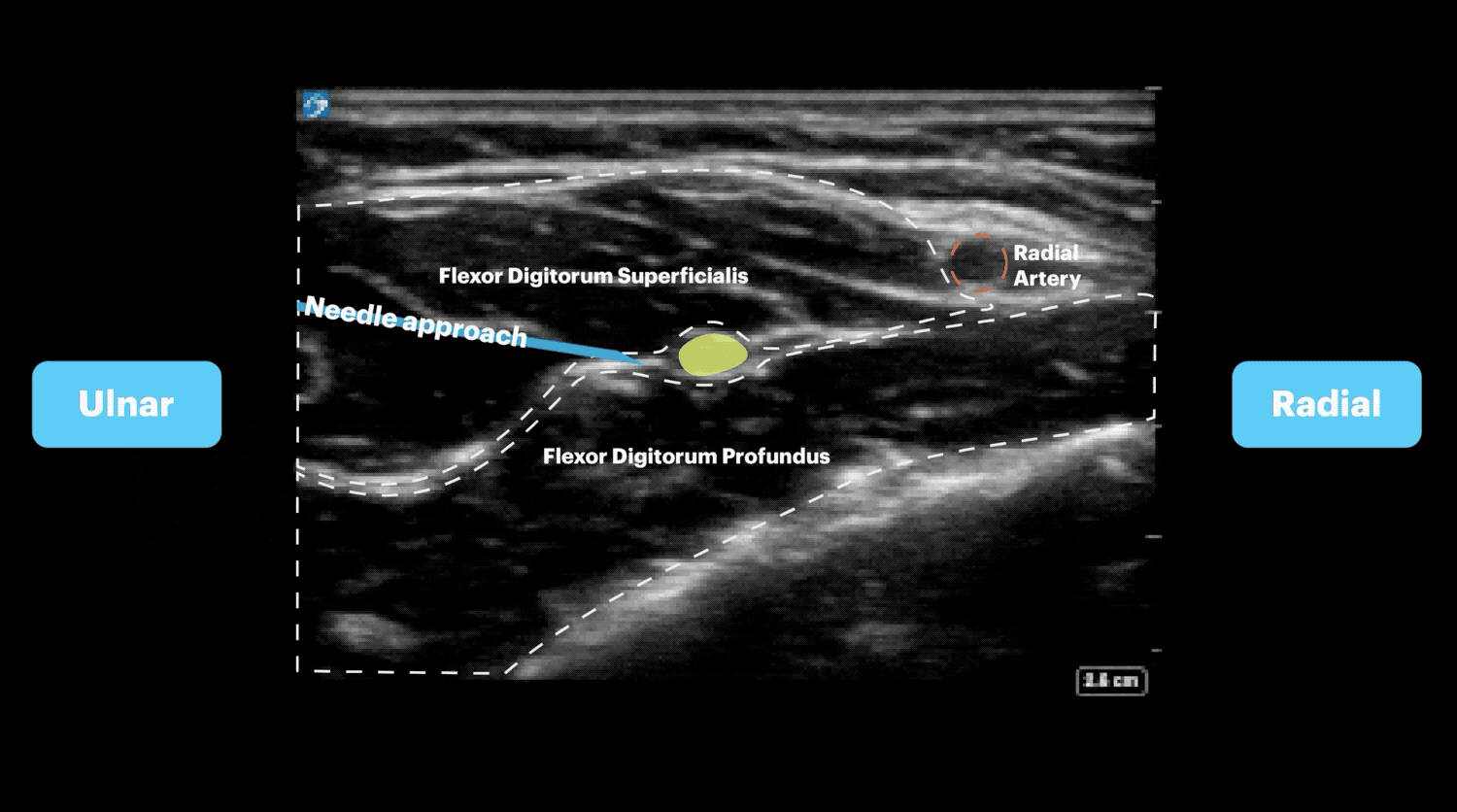
- The hyperechoic structure found in the fascial plane between the flexor digitorum superficialis and flexor digitorum profundus muscles is the median nerve.
- Insert the needle in-plane until the needle tip is adjacent to the nerve.
- Hydrodissect 1-2 mLs of anesthetic to confirm placement, then inject anesthetic until the nerve is surrounded.
Examples