Indications
- Humerus fracture
- Lacerations or abscesses of upper arm and deltoid
- Shoulder dislocation
Contraindications
- Infection overlying injection site
- Allergy to local anesthetic
- Severe lung disease: Risk of unilateral pneumothorax
- Phrenic nerve dysfunction: Specifically contralateral phrenic nerve dysfunction, due to the risk of unilateral paralysis
- Vascular injury/injection: There are many large vessels that serve as landmarks so color doppler and negative aspirations are essential
Equipment
- 10-15cc of local anesthetic of choice
- 18-22G needle
- Syringe
- Saline Flush
- Cleansing solution
- Ultrasound with linear transducer
- Ultrasound transducer sterile cover
Prepration
Position
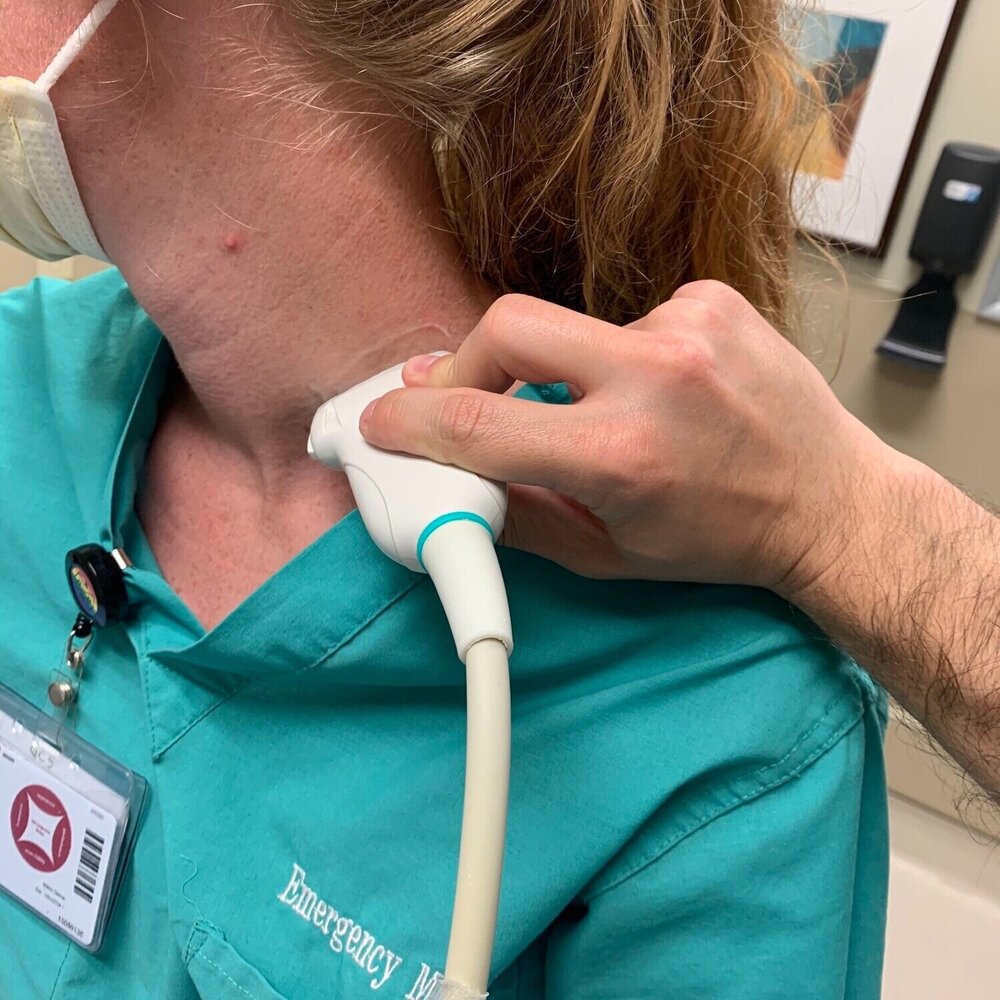
Patient is supine or sitting up slightly with the head to the contralateral side. Transducer is placed 2-3cm superior to the midpoint of the clavicle, or slightly superior to the external jugular vein if it can be appreciated.
Ultrasound
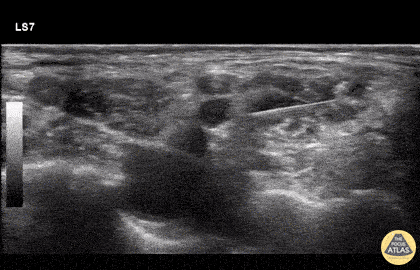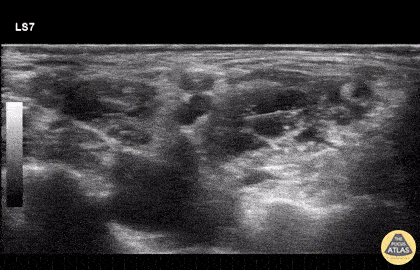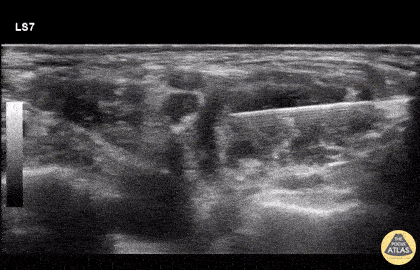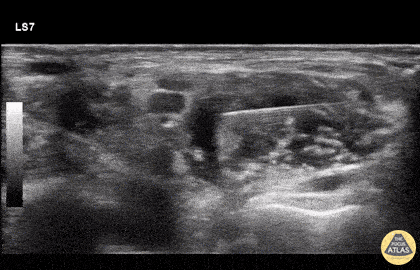
Landmarks
Approach #1
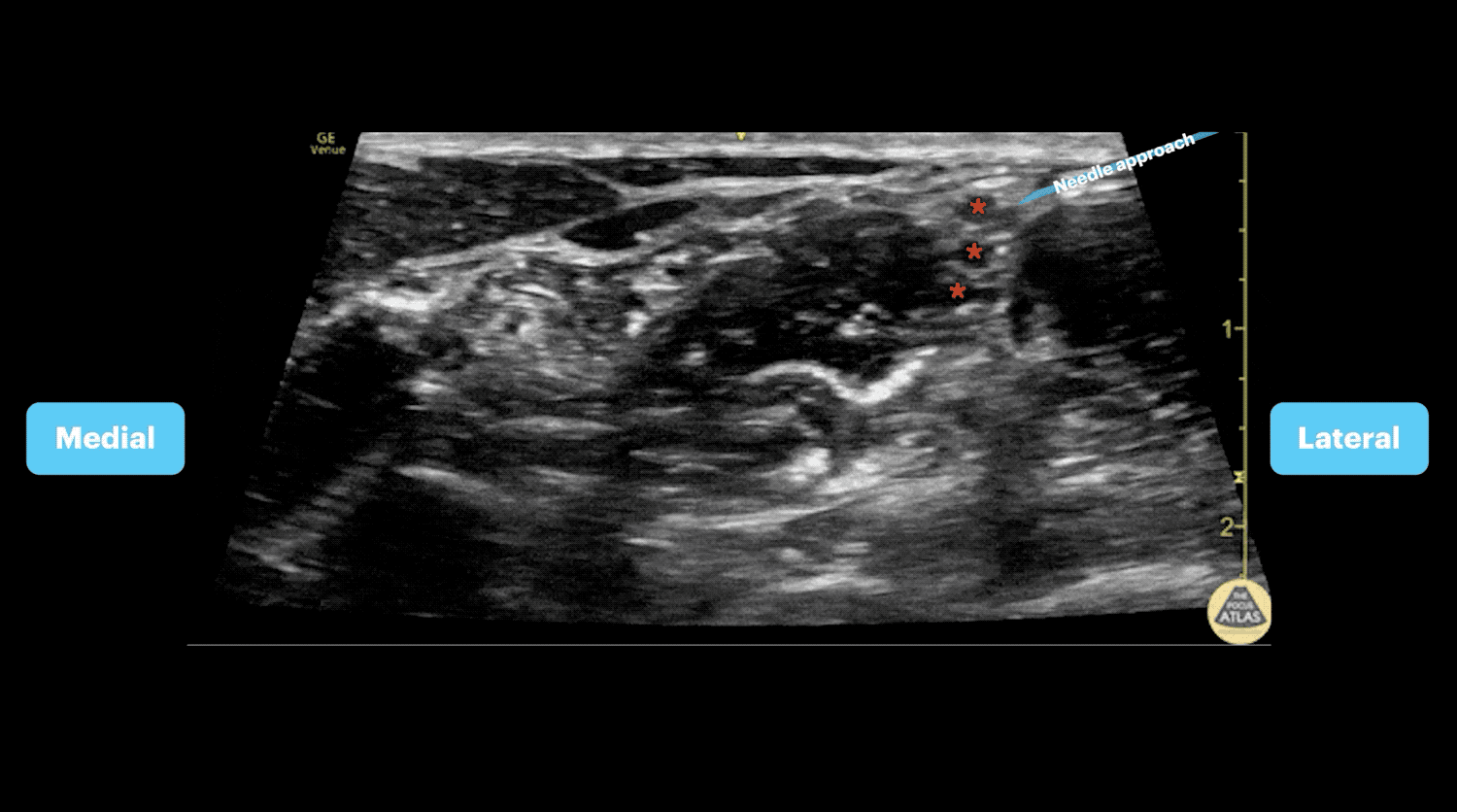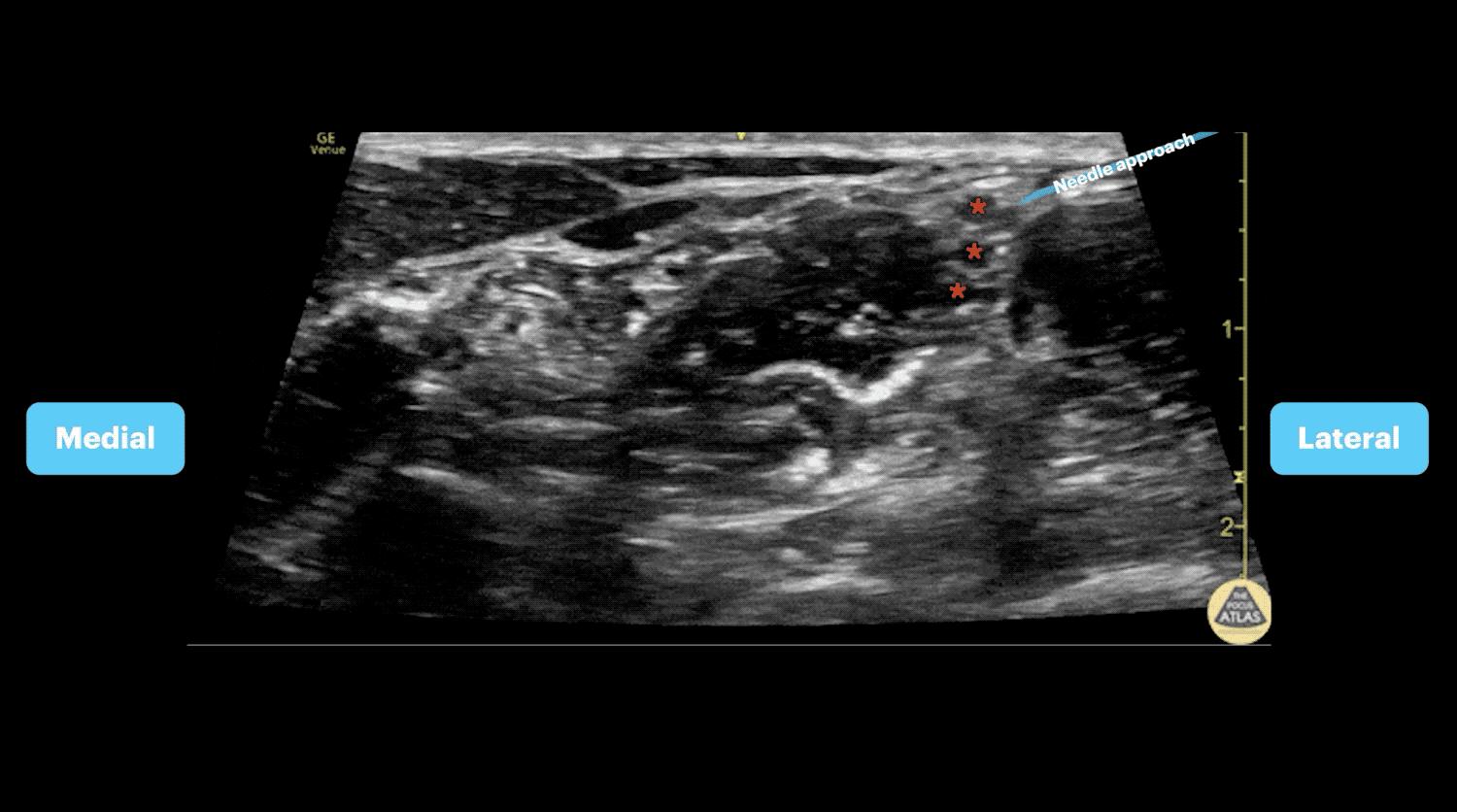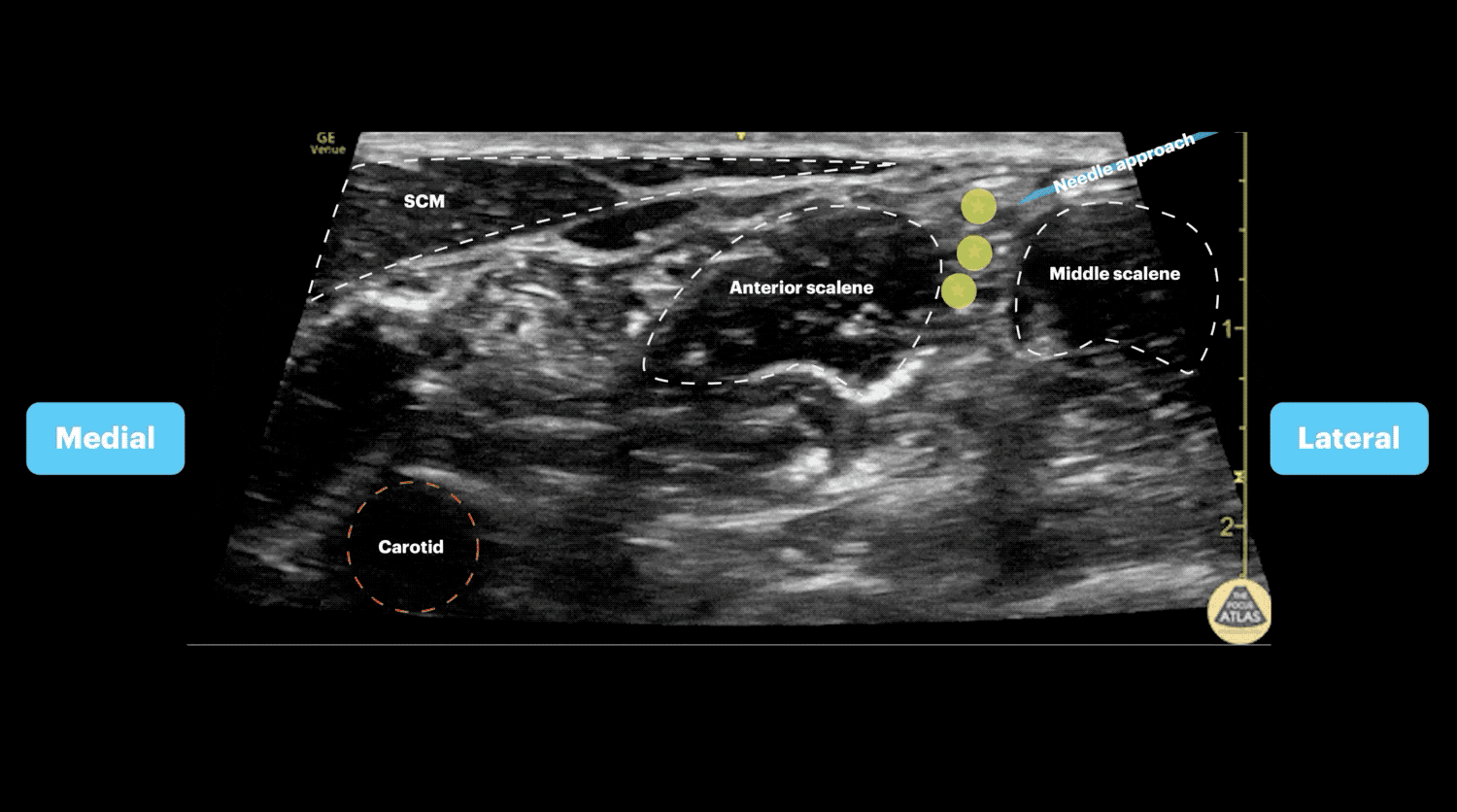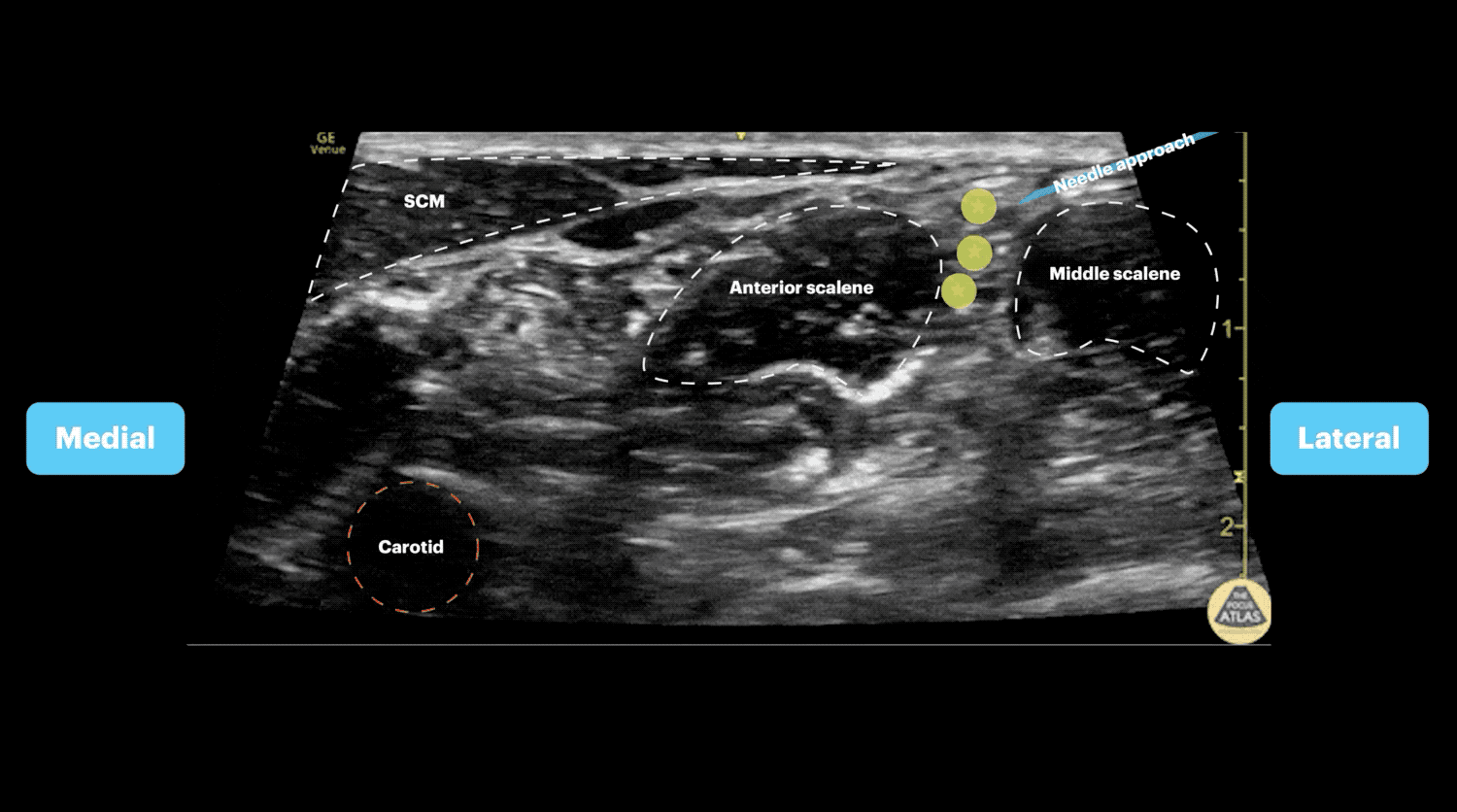
- The carotid artery can be identified deep to the sternocleidomastoid
- Slide posteriorly until a stack of cords is seen in between the anterior and middle scalenes.
Approach #2
- Identify the subclavian artery in the supraclavicular fossa
- Trace the brachial plexus up into the interscalene space.
Technique
- In-plane needle visualization
- Advance needle from lateral to medial towards the vertical stack of cords between the anterior and middle scalene muscles (interscalene space)
Example