Indications
- Hand laceration or injury
Contraindications
- Infection overlying injection site
- Allergy to local anesthetic
Considerations
- If performed above the elbow, the radial nerve contains both sensory and motor nerves, and blockade will result in a wrist drop
Equipment
- 5cc of local anesthetic of choice
- 25-27G needle
- Saline Flush
- Cleansing solution
- Ultrasound with high-frequency linear transducer
- Ultrasound transducer sterile cover
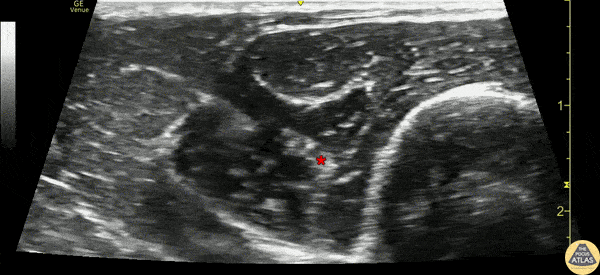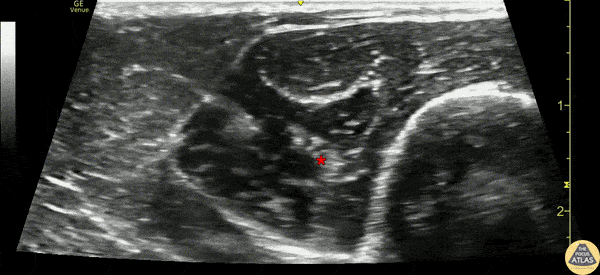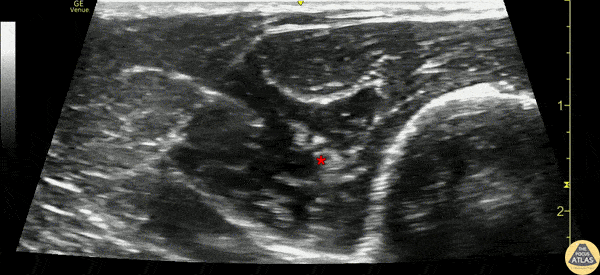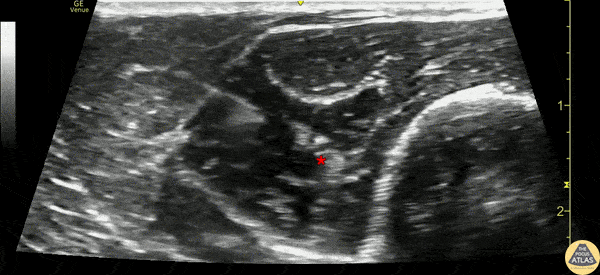
Ultrasound
Approach #1 (Elbow)

- Position arm extended or held over the abdomen with elbow flexed
- Place linear transducer transversely 4-5 cm proximal to the elbow, at the posterolateral aspect
- Identify the radial nerve adjacent to the humerus laterally, between the brachioradialis and brachialis muscles
- Verify that the nerve does not lie in close proximity to the brachial artery, as this may be the median nerve
- Surround target with local anesthetic
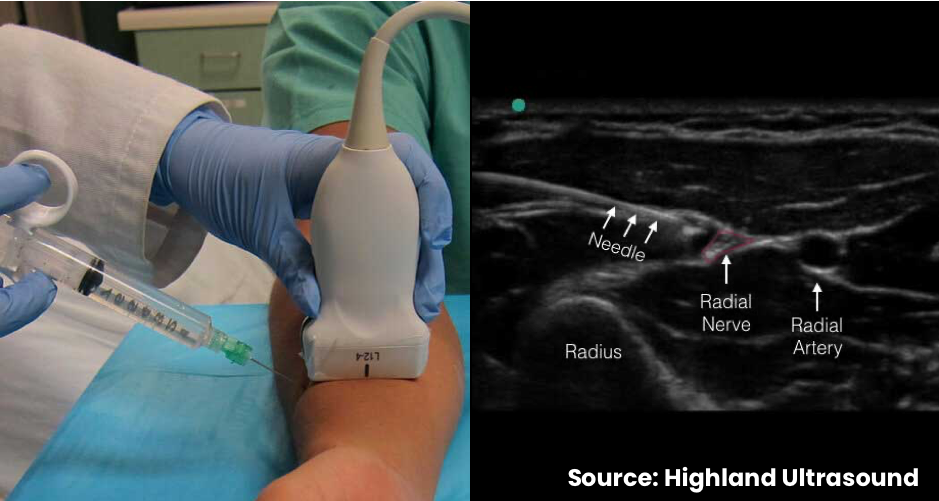
Approach #2 (Wrist)
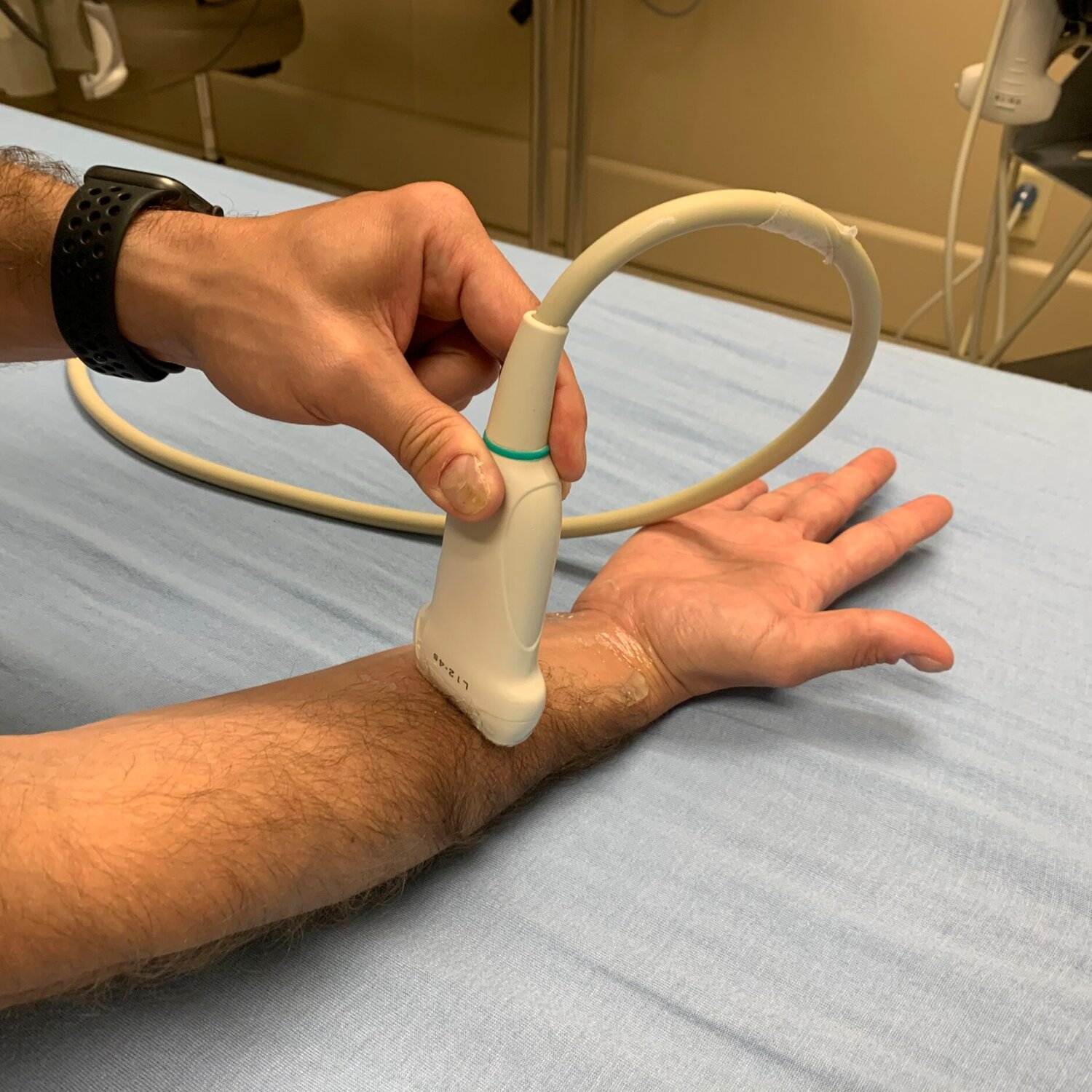
- Position with the forearm supinated
- Place the transducer in a transverse orientation 3-4 cm proximal to the volar wrist
- Locate the radial artery, identify the radial nerve which should be radial to the artery
- If the nerve is too close to the artery, trace proximally, where the nerve separates from the artery
- Surround target with local anesthetic
Examples